Solid Foundations: Building Right with Soil Investigation

Introduction
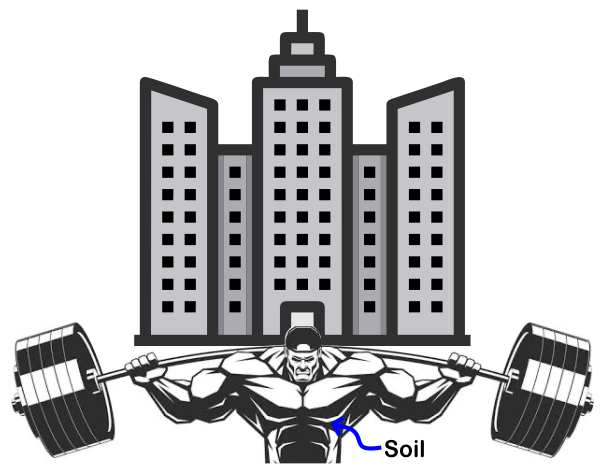
When embarking on a construction journey, the significance of solid foundations cannot be understated. These foundational underpinnings serve as the bedrock upon which our architectural aspirations take shape, and their strength is the ultimate determinant of a structure’s durability. At the heart of this crucial undertaking lies the invaluable practice of soil investigation – a process that delves deep into the earth’s composition to inform construction decisions to ensure stability. In this article, we’ll unearth the intricacies of soil investigation and explore how it lays the groundwork for a sturdy and successful construction venture. So, grab your hardhat and let’s dig into the world of solid structures and understand how soil investigation is the cornerstone of building right.
Setting the Stage: The Importance of Strong Foundations
Picture a towering skyscraper or an intricate bridge – their towering heights and sprawling spans owe their stability and longevity to the very first step of construction: building a strong foundation. Just as a giant oak tree’s strength lies in its roots, the resilience of any structure hinges upon the quality of its foundation. This is where soil investigation emerges as a guiding light, illuminating the path to a firm and secure start for your building.
The Role of Soil Investigation in Construction Success
Soil investigation is the unsung hero of construction – a process that ventures deep into the earth’s embrace, unravelling its mysteries and extracting essential knowledge. This knowledge becomes the cornerstone of informed decisions, shaping the blueprint of every architectural endeavour. Soil investigation is the art and science that transforms mere ideas into tangible, robust structures.
What is Soil Investigation and Why Does It Matter?
At its core, soil investigation is a comprehensive study of the earth beneath our feet. It involves delving into the intricate layers of soil, examining its composition, behaviour, and characteristics. This investigative journey is not only about understanding the ground; it’s about laying the groundwork for a stable and enduring construction.
The Science Beneath: Exploring Soil Composition and Properties
Beneath the surface lies a complex world of soil types – from dense clays to loose sands, each with its unique properties and behaviours. Soil investigation unlocks this hidden realm, analysing factors like grain size, moisture content, and density. By deciphering these characteristics, engineers gain insights into how the soil will interact with the weight of the structure and external forces.
Types of Soil Tests: From Boring to Permeability
The toolkit of soil investigation is as diverse as the soils it explores. And they are categorized under two techniques:
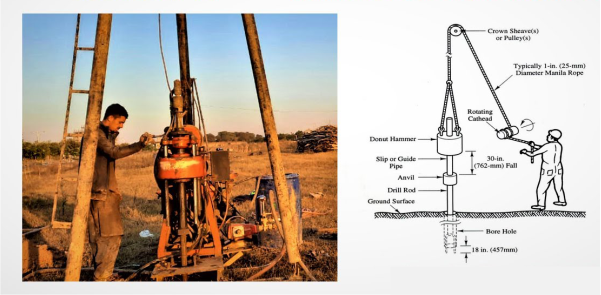
(1) Boring techniques: extract soil samples from various depths, providing a vertical cross-section of the earth’s layers.
By utilizing a range of tests, soil investigation reveals a comprehensive picture of the terrain beneath.
Unearthing Benefits: Why Soil Investigation is Crucial
(1) Ensuring Structural Integrity: How Soil Investigation Prevents Settlement
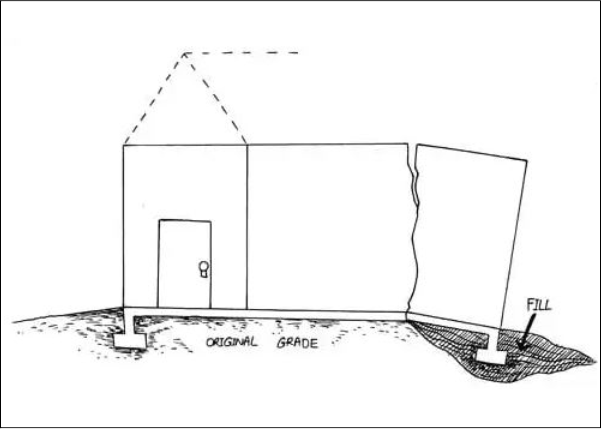
Picture a building that leans or tilts over time – this is a result of uneven soil settlement. Soil investigation identifies areas susceptible to such settlement, empowering engineers to implement measures that counteract this natural phenomenon. By pre-emptively addressing settlement, soil investigation forms the foundation of a structure’s longevity.
(2) Navigating Groundwater: Mitigating Risks through Proper Analysis
Groundwater, though invisible, can significantly impact construction projects. Excessive moisture weakens soil, potentially leading to instability. Soil investigation evaluates groundwater levels and flow patterns, allowing engineers to design foundations that expertly manage water ingress and prevent issues like erosion.
(3) Tailoring Designs: Adapting Building Plans to Soil Characteristics
Just as a tailor crafts a garment to fit perfectly, engineers must tailor building designs to suit the unique attributes of the soil. Soil investigation provides precise specifications, guiding the creation of foundations that distribute loads evenly and mitigate external pressures. This tailoring ensures that structures stand strong even in the face of adversity.
(4) Stability Matters: Preventing Slope Failures with Comprehensive Studies
In regions with varied terrain and slopes, soil investigation becomes a critical tool for ensuring stability. By analysing soil strength, shear characteristics, and erosion potential, engineers design support systems that prevent slope failures. This proactive approach safeguards not only the construction but also the environment it interacts with.
The Soil Investigation Process
(1) Step by Step: From Site Selection to Sampling
The journey of soil investigation begins with strategic site selection. Various factors, including topography and intended use, influence this decision. Once a site is chosen, samples are collected through techniques like boreholes or test pits, revealing the soil’s composition at different depths.
(2) Laboratory Analysis: Decoding Test Results and Implications
Collected samples find their way to the laboratory, where they undergo meticulous analysis. This phase uncovers a wealth of information, from soil classification to load-bearing capacity. Engineers decode these results to develop a comprehensive understanding of soil behaviour and its implications for construction.
Choosing the Right Techniques
(1) Geotechnical Drilling: Going Deep to Assess Soil Layers
Geotechnical drilling is a plunge into the heart of soil science. Drilling rigs penetrate the earth, extracting soil cores that offer insights into subsurface layers. This method helps experts map soil variations, identify potential weaknesses, and strategically plan construction activities.
(2) In-Situ Testing: Real-Time Data Collection for Accurate Insights
In-situ testing takes the investigation to the source, delivering real-time data on soil properties without disturbing the ground. Techniques like the Standard Penetration Test (SPT) and the Cone Penetration Test (CPT) enable engineers to assess soil behaviour directly, ensuring precise and reliable insights.
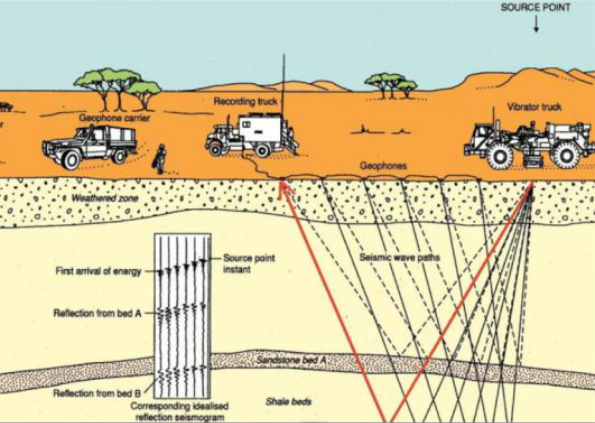
(3) Geophysical Methods: Mapping Subsurface Features
Also known as Non-Destructive Geophysical Soil Investigation Methods harnesses technology in testing soil. Geophysical methods employ tools like ground-penetrating radar and seismic surveys to map subsurface features. These non-invasive techniques create detailed images of the soil’s internal structure, aiding in the identification of anomalies and potential challenges.
Uses of Interpreted Results
(1) Soil Bearing Capacity: Determining Load-Bearing Capacity for Safe Construction
Imagine constructing a skyscraper without knowing how much load the soil can bear – it’s like building on uncertainty. Soil investigation exposes the bearing capacity of a soil, empowering engineers to calculate appropriate foundation dimensions and types. This understanding ensures a structure’s sturdiness under varying loads.
(2) Settlement Analysis: Predicting and Managing Foundation Settling
Predicting settlement is akin to foreseeing a building’s future stability. Soil investigation informs settlement analysis, allowing engineers to anticipate how different sections of the foundation will settle over time. This insight helps implement measures to minimize differential settling, safeguarding the structure against potential damage.
(3) Shear Strength Analysis: Assessing Soil Stability and Slope Protection
Shear strength, a soil’s ability to resist sliding along planes, is crucial for stability, especially on slopes. Soil investigation’s shear strength analysis guides engineers in designing foundations and retaining structures that prevent slope failures, supporting overall stability of the structure being built.
Mitigating Risks and Ensuring Safety
Foundation Design: Incorporating Soil Investigation Findings into Designs
Armed with an abundance of soil data, engineers embark on the creative process of foundation design. Soil investigation findings guide material selection, footing configurations, and reinforcement placement. The result? A design that not only supports the structure but enhances its resilience.
Risk Management: Addressing Potential Challenges and Pitfalls
Construction is a symphony of moving parts, and soil investigation serves as the conductor. By revealing potential challenges, such as soil liquefaction or subsidence, it equips engineers to proactively address these concerns, ensuring construction proceeds smoothly and securely.
Cost-Effectiveness: How Soil Investigation Saves Money in the Long Run
While soil investigation may seem like an upfront expense, it’s an investment in construction longevity. By identifying and mitigating risks early, projects avoid costly delays, repairs, or even total failure. The cost of thorough soil investigation pales in comparison to the potential expense of neglecting it.
Reduces Assumption: Soil Investigation Prevents trial by Error
Soil investigation also prevents the engineer from assuming foundation type to be used. Which could be most times the consideration will be to take a more conservative assumption, thereby forcing you to build a more expensive foundation. Other times a totally wrong foundation type is assumed which may lead to differential settlements or total collapse
Real-World Examples
Success Stories: Projects Aided by Comprehensive Soil Investigation
Across the globe, construction marvels stand as testimonials to the transformative power of soil investigation. From towering skyscrapers to simple duplexes, these projects showcase the impact of informed decisions based on thorough soil analysis. They underscore the pivotal role that soil investigation plays in construction achievements.
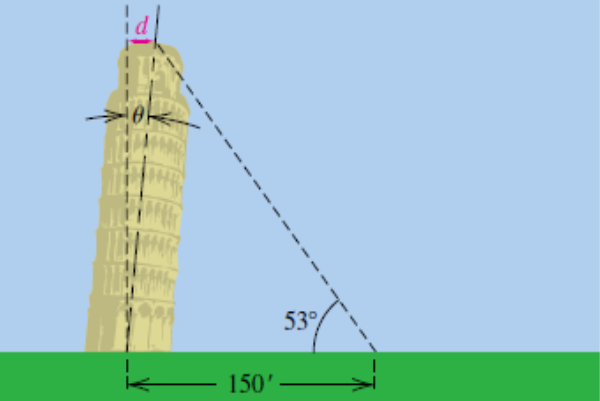
Learning from Mistakes: Case Studies on the Consequences of Skipping Soil Investigation
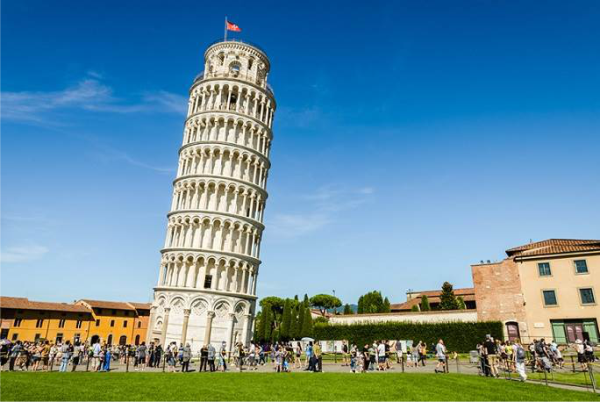
As history has shown, the consequences of ignoring soil investigation can be dire. The infamous leaning Tower of Pisa serves as a reminder of what can occur when this essential step is overlooked. Such cautionary tales emphasize that cutting corners on soil investigation can lead to structural instability and financial losses.
Conclusion
Building for the Future: The Lasting Impact of Solid Foundations
In an ever-evolving world, where innovation and progress shape the horizon, the art and science of building remain timeless. Just as the ancient architects recognized the significance of strong foundations, today’s builders continue to harness the wisdom of the past while embracing modern techniques. Soil investigation is the bridge that connects these eras, allowing us to fuse ancient wisdom with cutting-edge knowledge.
As you embark on your own construction journey, remember the invaluable role that soil investigation plays. It’s more than just a process; it’s a story written in layers of earth, waiting to be deciphered by those who seek to build right. So, whether you’re planning a modest home or a towering skyscraper, pause to consider the ground you stand on. For beneath that surface lies a world of secrets, waiting to be uncovered – secrets that hold the key to your construction’s strength, stability, and success.
Follow Our Social Media
Call Us Now
Come Visit us At:
Tulip 6, Prime Water Gardens II, Lekki, Lagos. Nigeria



















2 Responses
Awesome write up! Thanks
Thank you